Six Sigma: Introduction
- sujonodamario

- Mar 28, 2021
- 2 min read
Industrial Systems are a network of entities that creates products or services with added value from the raw materials. To maintain consistency and quality of products or processes, a method of Quality Control needs to be implemented.
Quality Control is an activity to measure qualities of products, compare with standardized specifications, and provides adjustments when any difference occurs.
Apart from maintaining the qualities, it is also essential to improve the qualities themselves since it also reduces the operational costs. One popular method to enhance qualities is called Six Sigma.
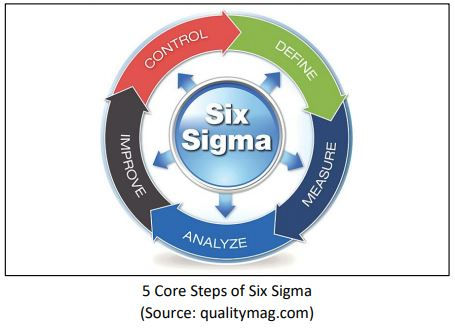
According to Introduction to Engineering Statistics and Six Sigma by Allen (2006), Six Sigma is an organized and systematic problem-solving method for strategic system improvement and new product and service development that relies on statistical methods and the scientific method to make dramatic reductions in customer-defined defect rates and/or improvements in key output variables.
Six Sigma statistically aims to reduce a defects rate of a process to fewer than 3.4 defects per one million opportunities; However, Six Sigma is also commonly implemented to general-approach system improvement due to its concise and clear steps namely DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control).
Define Step is the process of defining problems, objectives, and strategies to achieve those objectives. One important measurement to analyze in this step is Critical-to-Quality (CTQ), which contains information on variables that have a significant influence on quality based on consumer needs. Measure Step is a data collecting and performance measurement process for the current system.
This step provides insights into how well the current system operates in comparison to the desired standard. Measure step also analyzes how stable the process is since it is ineffective to apply adjustments and improvement when the process itself is volatile.
Analyze Step is the process of examining the relationships of variables to determine the problems’ root causes. In other words, analyzing current data necessary to achieve the objectives happens during this phase. Multiple tools are useful for determining relationships and root causes such as Cause-and-Effect Diagram, Pareto Analysis, Failure Mode Effects Analysis (FMEA), and many other tools.
Improve Step is the process of designing and implementing improvement methods based on data and information from the previous step. The type of improvements ranges from buying a new machine, rearranging workspace, redefine a whole standard procedure, to simply providing a simple screwdriver to each laborer. The most important part is recording the data after implement the changes that is critical for the next Step.
Control Step is the process of monitoring the performance of one process after the implementation to sustain improved results. Similar performance measurement in Measure Step also conducted here and then compared to the data before the implementation.
This comparison grants information on how well these changes affect system and whether they solve the problems and/or reach the objectives stated in Define Phase.




Comments